Socket to Me: How Much Does It Cost to Install or Replace Electrical Outlets?
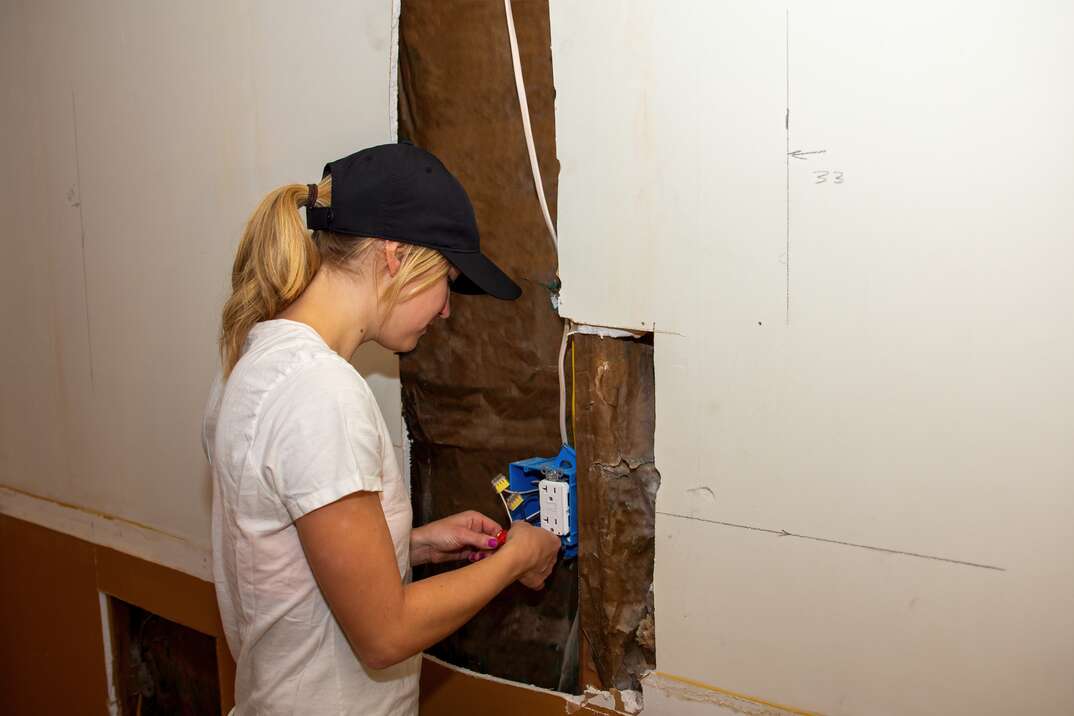

Whether you need to add new electrical outlets to your home or upgrade the ones you already have, the process is relatively easy and affordable. While some homeowners can replace electrical outlets themselves without much difficulty, it’s advisable to seek the assistance of an experienced electrician or handyman if you have any doubts.
This May Also Interest You: How to Replace an Electrical Outlet: A Step-by-Step Guide
The type of outlet and scope of the work involved will have an impact on the final price. Read on to learn more about the cost of installing an additional electrical outlet.
Installing an Electrical Outlet
For a completely new outlet installation, you will need to cut a hole in the wall to seat the metal housing. Additional wiring may need to be fished through the walls as well. The cost to install a standard electrical outlet usually falls between $125 and $175 (CAD 168 and 235) for parts and labor, according to Forbes.
However, depending on where you live and the complexity of the job, installing an outlet can cost as much as $500 (CAD 671). Although costs can vary by location, electricians typically charge about $125 (CAD 168) per hour, according to Family Handyman. Unlicensed apprentices may assist on jobs that require additional workers for about $95 (CAD 127), depending on where you live.
According to Forbes, many standard electrical receptacles run between $3 and $5 (CAD 4 and CAD 7). Most faceplates are very cheap as well — costing under $2 (CAD 3) in some cases, based on data from The Spruce. The brunt of the cost lies in fishing new wiring through the wall to meet the outlet.
Replacing Electrical Outlets
The cost to replace existing electrical outlets typically also falls between $125 to $175 (CAD 168 and 235), and the task takes little time for professionals to complete. This is a quick and easy project, assuming the electrical wiring from the old outlet is intact. If the ground wire is severed or new cables need to be fished to the outlet, you can expect to pay around $27 (CAD 36) per linear foot. This can typically add $500 to $1,200 (CAD 671 to CAD 1,610) to the project.
Working with electricity can be dangerous. If you prefer to replace electrical outlets yourself, make sure the power is turned off from the breaker box before getting started. It is advisable to use a voltmeter to double-check that the outlet isn't live before you touch any wires.
Using a screwdriver, remove the faceplate from the wall and the screws that brace the receptacle to the outlet box. Once the old outlet is removed, match up the positive, negative and ground wires to the connections on the replacement receptacle. After this is done, turn the power back. The job is complete! The cost of this DIY task is little more than $5 for the new receptacle and faceplate.
Three-Prong Outlets
Three-prong outlets are required to accommodate most modern appliances. Some older homes may not have three prongs on all outlets because electrical codes changed in 1962. Replacing outdated receptacles is fairly straightforward, but your electrician or handyman may need to run a new ground wire from the outlet to the breaker. All things considered, this can cost anywhere between $130 and $170 (CAD 174 and CAD 228) for each outlet, according to Tools Week.
GFCI Outlets
These outlets will automatically shut off if a fluctuation in power is detected. GFCI outlets are designed to protect people from electrocution, especially in environments like bathrooms and kitchens where water is present. GFCI outlets are easy to distinguish due to the “reset” and “test” buttons located between the sockets. According to Bob Vila, installing a GFCI outlet will cost $210 (CAD 282) on average, but if new wiring needs to be run, this price can double.
More Related Articles:
- Types of Electrical Outlets
- 4 Steps for Proper Electrical Maintenance
- Hiring for Wiring? 5 Tips for Finding a Trusted Electrician
- How Much Does It Cost to Replace an Electrical Panel?
- Electric Car Charging at Home: Everything You Need to Know
USB Outlets
In today’s digital world, keeping our devices charged is a huge priority. Installing electrical outlets with traditional USB or modern USB-C plugs is useful for charging cellphones and tablets, especially if you've lost that little charging block. Family Handyman notes that USB outlets are a little more expensive than their conventional counterparts, costing between $20 and $50 (CAD 27 and CAD 67). For professional installation, most people will pay the same price as installing a regular outlet. The total cost is between $125 and $175 (CAD 168 and CAD 235).
Childproof Faceplates
To ensure the little ones are protected from electrical outlets, childproof faceplates are an affordable solution. Installation is pretty straightforward; usually, you'll just need a screwdriver. Fixr says prices will vary on these, but most homeowners will find what they need for $3 to $15 (CAD 4 to CAD 20). Some electrical receptacles have integrated child safety mechanisms, but these tend to cost more than conventional faceplates.
Factors That Influence Cost
The location of a new outlet could have an impact on the overall price. In general, the more cables that need to be run, the more expensive the project will be. Additionally, various outlets are rated to handle different loads. For larger appliances like washing machines, a 220V/240V outlet is needed. These outlets are more challenging to install. It typically costs around $300 (CAD 403) to get the job done, according to Forbes.
If electrical repair work needs to be done to support the new outlets, this will also increase the cost. Most professionals charge around $27 (CAD 36) per linear foot of new wiring. In some cases, your home’s electrical service may need an upgrade to accommodate your new outlets. The cost of this project depends on the power demands of your home. For instance, installing the infrastructure to support 400-amp electric service can end up costing as much as $5,000 (CAD 6,710).
All CAD conversions are based on the exchange rate on the date of publication.